Introducing Tornado Tracker, an indispensable tool for navigating the treacherous realm of tornadoes. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of tornado tracking, warning systems, forecasting, and safety measures, empowering individuals to stay informed and prepared in the face of these formidable weather events.
From radar technology to storm spotters, the methods employed to track tornadoes are as diverse as they are essential. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each approach enables us to piece together a more accurate picture of these unpredictable storms.
Tornado Tracking Methods
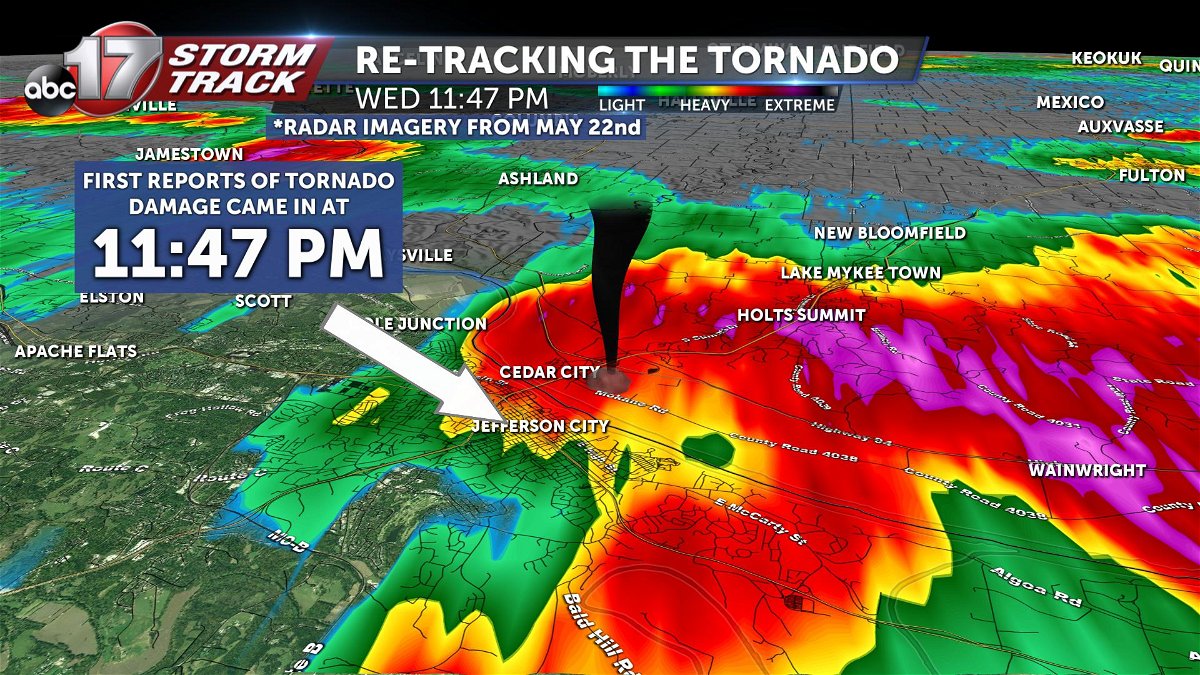
Accurate tornado tracking is crucial for timely warnings and safety measures. Various methods are employed to monitor and track tornadoes, each contributing to a comprehensive understanding of these dangerous weather events.
Radar
- Uses electromagnetic waves to detect precipitation and wind patterns.
- Provides real-time data on tornado location, intensity, and movement.
- Doppler radar can measure wind speeds and direction, helping to identify tornado circulation.
Satellite Imagery
- Provides a broader view of weather patterns and cloud formations.
- Can detect large-scale atmospheric conditions favorable for tornado development.
- Helps in identifying potential tornado-producing thunderstorms.
Storm Spotters
- Trained volunteers or meteorologists who observe and report tornadoes firsthand.
- Provide valuable ground-level information on tornado characteristics and behavior.
- Help verify radar data and fill in gaps in coverage.
Tornado Warning Systems: Tornado Tracker
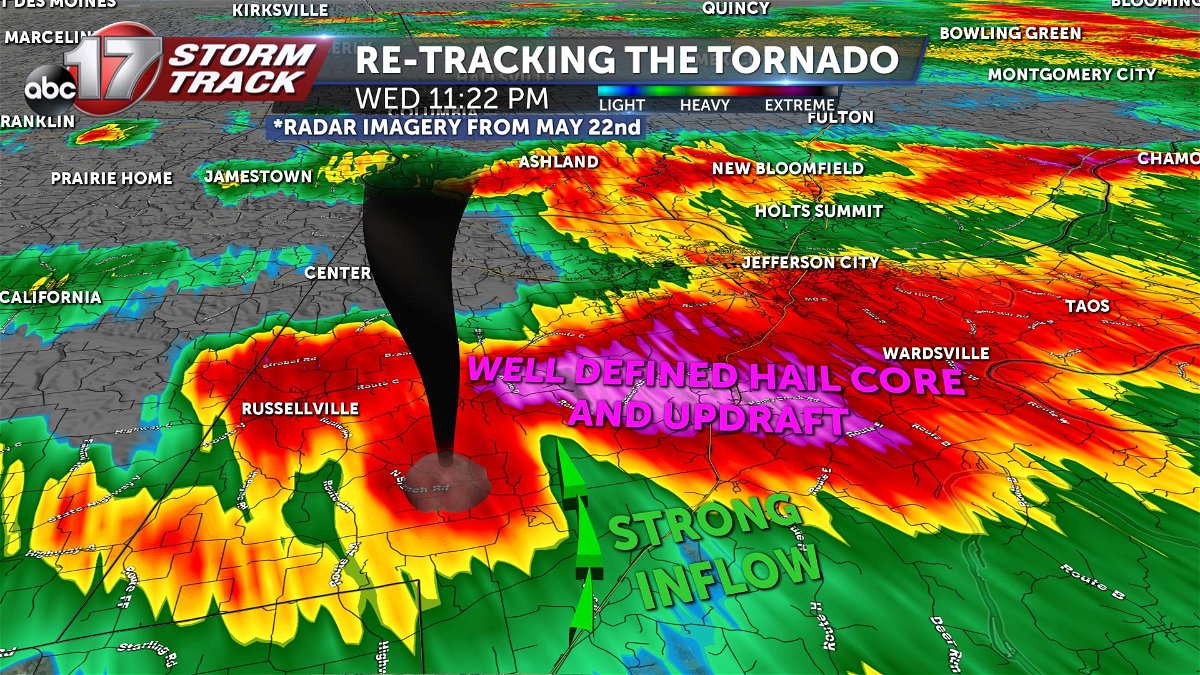
Early and effective warning systems are essential for minimizing the impact of tornadoes. Various systems are in place to alert the public and emergency responders.
Public Alerts
- Issued by the National Weather Service (NWS) through multiple channels, including TV, radio, and mobile notifications.
- Provide real-time information on tornado warnings, including location, direction, and intensity.
- Encourage immediate protective actions, such as seeking shelter.
Sirens
- Outdoor warning devices that emit a distinctive sound when a tornado warning is issued.
- Provide an audible alert to people outdoors or in areas with limited access to other warning systems.
- May not be effective in all situations, such as during severe weather or in remote areas.
Mobile Notifications, Tornado tracker
- Sent directly to mobile devices through apps or SMS.
- Provide immediate and personalized alerts based on location.
- Can include detailed information and safety instructions.
Tornado Forecasting and Prediction
Predicting tornadoes is a complex and challenging task, but advancements in weather science and technology have improved forecasting capabilities.
Atmospheric Conditions
- Certain atmospheric conditions, such as high wind shear, instability, and moisture, are favorable for tornado development.
- Meteorologists analyze weather data to identify areas with a higher risk of tornadoes.
- Numerical weather prediction models simulate atmospheric conditions to forecast potential tornado activity.
Weather Patterns
- Specific weather patterns, such as supercell thunderstorms and squall lines, are often associated with tornadoes.
- Meteorologists track these patterns and monitor their evolution to anticipate tornado formation.
- Ensemble forecasting uses multiple model runs to assess the uncertainty in tornado predictions.
Tornado Safety and Preparedness
Knowing what to do before, during, and after a tornado can save lives. Preparation and safety measures are crucial for minimizing risks.
Before a Tornado
- Develop an emergency plan and practice tornado drills.
- Identify a safe shelter, such as a basement or interior room on the lowest floor.
- Secure loose objects and have a disaster kit ready with essential supplies.
During a Tornado
- Seek immediate shelter and stay low.
- Avoid windows and exterior walls.
- Cover your head and neck with a blanket or pillow.
After a Tornado
- Stay away from damaged areas and downed power lines.
- Report any injuries or damage to authorities.
- Follow instructions from emergency responders.
Tornado Research and Technology
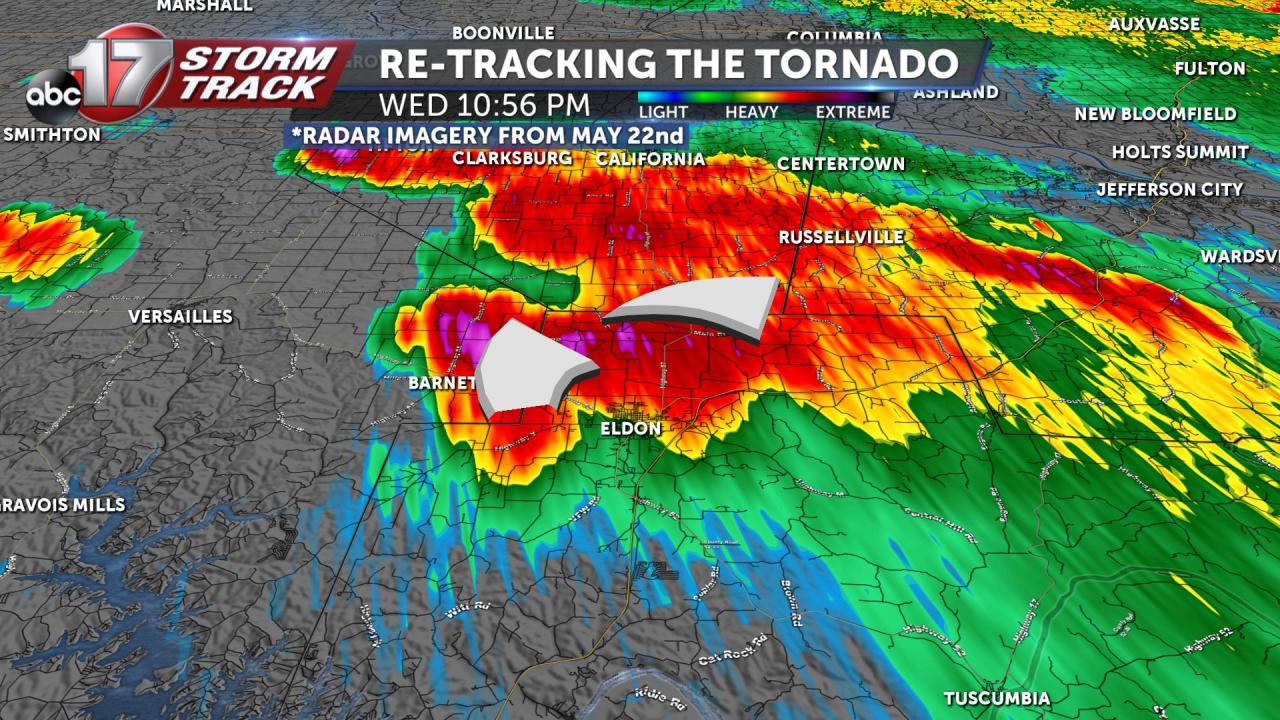
Ongoing research and technological advancements are enhancing our understanding of tornadoes and improving tracking, forecasting, and warning systems.
Drones
- Unmanned aerial vehicles can collect data within tornadoes, providing valuable insights into their structure and behavior.
- Help in identifying tornado characteristics, such as intensity and wind speeds.
- Can be used to deploy sensors and instruments for real-time monitoring.
Artificial Intelligence
- Machine learning algorithms can analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns and improve tornado predictions.
- Help in automating tornado detection and tracking, reducing human error.
- Can be used to develop early warning systems based on real-time data.
Final Wrap-Up
Tornado Tracker serves as a vital resource, not only for weather enthusiasts but for anyone seeking to stay safe and informed during tornado season. By harnessing the latest advancements in technology and scientific understanding, we can mitigate the risks associated with these devastating storms and emerge better prepared to face them.
Questions and Answers
What is the most accurate method of tornado tracking?
Radar technology, combined with data from satellites and storm spotters, provides the most comprehensive and accurate means of tracking tornadoes.
How are tornado warnings issued?
Tornado warnings are typically issued by the National Weather Service based on radar data and reports from storm spotters. Warnings are disseminated through various channels, including public alerts, sirens, and mobile notifications.
What should I do if I receive a tornado warning?
Seek shelter immediately in a sturdy building, preferably below ground level. Stay away from windows and exterior walls, and be prepared to ride out the storm.